Difference between revisions of "Trashure Island - a proposal for a circular economy in Tropicana"
Rümeysa Önal (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == the circular | + | {{Article |
| + | |Image=tropicaldream.jpg | ||
| + | |Caption=Tropicana, a true aquatic paradise | ||
| + | |Summary=New strategies such as the Blue Economy (Gunter Pauli) and Sustainism (Michael Schwarz and Diana Krabbendam) propose solutions to ecological, economic and social crises. These movements see local materials (waste products, local communities & expertise) as valuable assets, transforming linear processes into circular processes and valuing long-term performance over short-term gain. What are working business models for these types of reorganisations? | ||
| + | |Article=Author: Students Masterclass The Circular Economy | ||
| − | Tropicana | + | === Tropicana, from a dream in decay to an opportunity for change? === |
| + | Over the past century, most cities have become agglomerations of monofunctional districts which are basically disconnected from each other. Residential neighbourhoods, industrial estates, office complexes, farming districts and recreational areas are spatially delimited by administrative boundaries, making it harder to make good use of their mutual presence. The ever-increasing flow of goods, energy, water, food and even capital is disconnected from the location where these are created, contributing to endless transportation, traffic congestion, waste of energy and pollution. In a special masterclass at the WdKA Redesigning Business event (November 2014), an interdisciplinary group of students sought ways to promote the exchange between existing flows by making smart new connections: the main requirement of an ecosystem. The host of this masterclass was Rotterzwam, a local mushroom farming business which grows mushrooms on left-over coffee grounds. We used their business case as a starting point for a proposal in which a former sub-tropical swimming paradise is turned into a centre for innovation: sustainable, connecting and regenerative. | ||
| − | It | + | The masterclass took place in Tropicana, an iconic building on the river Maas in Rotterdam that was built in 1988. It was a promise of a tropical experience, a true aquatic paradise. The lack of maintenance and plans to redevelop it into an event centre meant that Tropicana closed its doors in the summer of 2010. Bankruptcy in 2011 meant that the redevelopment never happened and the building became a dream in decay. At the moment though, smaller scale, but maybe more interesting, developments are happening on the site. It now serves as a temporary location for various businesses and has a restaurant and a bar as well as facilities for roasting coffee and farming oyster mushrooms on left-over coffee grounds. Can this landmark become a metaphor for new ways of thinking, sharing, working and relaxing all with an important focus on recycling as well as on research into flows of goods, energy, water, food and even capital? Can we make smart connections between local surpluses, shortages and bottlenecks, thus creating new functions and business cases for Tropicana? |
| − | + | [[File:mcce afbeelding 2.jpg|From a sub-tropical paradise to a dream in decay]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==== Trashure Island ==== | |
| − | |||
| + | The city of Rotterdam has high ambitions for sustainability. Why not use Tropicana as a building that represents sustainable development and give the building back its iconic status?! Tropicana could become 'Trashure Island', an island which will share and show sustainable ideas, mainly focussing on how to reuse waste flows. This would create a circular economy. It will be an ecosystem consisting of a lab and a knowledge centre where local people can learn by doing and where innovation and experimentation can take place. This way the mindset of people can change and it will be a new kind of education. This results in BIY: a Blue It Yourself economy. The waste flows of a concert stage, which will soon be added to the building, and the restaurant will also be a part of the circular ecosystem. The building's waste flows and trash and unemployed people become the new gold. Trash becomes treasure. It is an innovative way of creating awareness for sustainability for the people of Rotterdam and eventually for the rest of the world. This way, people can be introduced to the blue economy in an innovative and educative way (further explained in our video & images) and presentation of a case study in which we present Treasure Beer, a new beer brand that could be consumed as well produced in Tropicana (see video advertorial). | ||
| − | + | {{#ev:vimeo|116853038}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
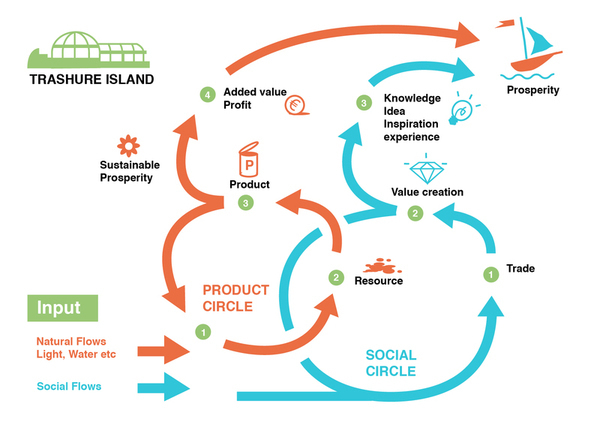
| + | [[File:mcce afbeelding 3.jpg|This schedule shows how the ecosystem functions and the flows that are a part of this system. It consists of a natural and a social flow. The natural flow has an input consisting of waste, sunlight, water and air. These flows enter the system and transform into products, made by different stakeholders. These stakeholders can benefit from each other's products, waste and other flows. A circular ecosystem will emerge in this setting. The social circle shows how people become input, and create knowledge and experience. The people that participate in the system transform energy into value. This value is very important for the social system of Rotterdam and can eventually reach the rest of the world. The value here is global knowledge, local awareness, and social prosperity through sustainable thinking.]] | ||
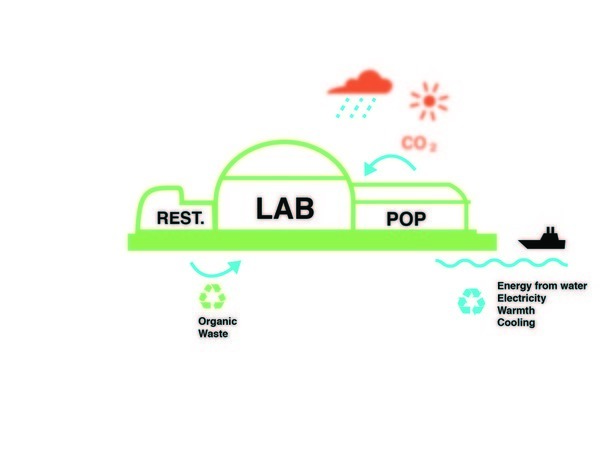
| − | [[ | + | [[File:mcce_hights.jpg|Trashure Island benefits from natural resources such as the sun, rain and water of the Maas that provide the building with energy and heat and regulates the temperature.]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:mcce_stream1.jpg|Flows of production; The leftovers of the restaurant can be recycled in the lab of Trashure Island and recreated into new products. The time and effort that will be invested in the building will make it possible to produce knowledge for the workers and visitors. This information and knowledge can be passed on to other people and so on.]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
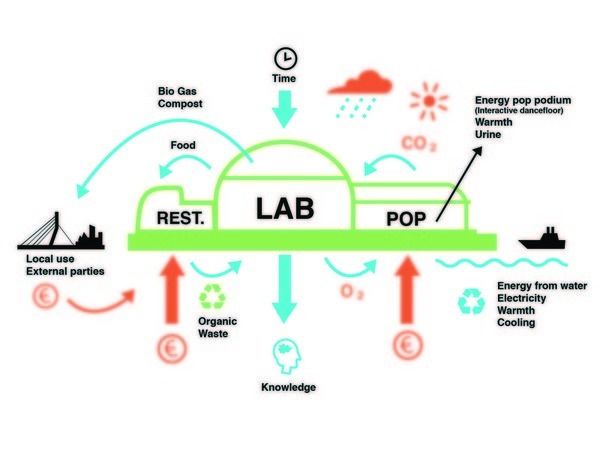
| − | [[ | ||
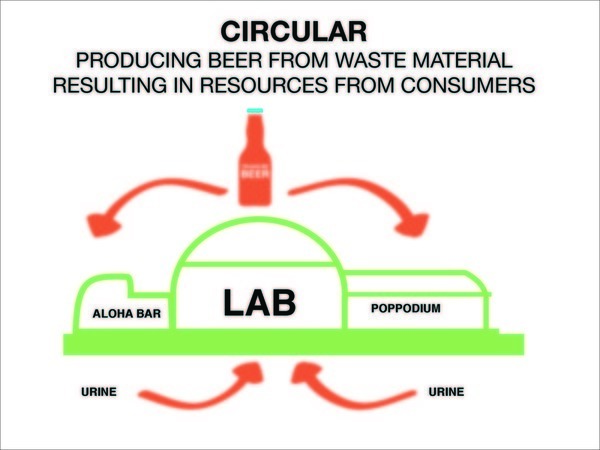
| − | + | [[File:mcce_stream2.jpg|The restaurant provides waste, urine (from which valuable phosphorous can be harvested) and thermic for the lab. The concert stage provides energy and CO2. The dance floor of the concert stage provides electricity that we use for production in the lab.]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | The restaurant provides | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:mcce_stream3.jpg|The lab provides the restaurant and concert stage with visitors, oxygen, food, drinks and energy.]] | ||
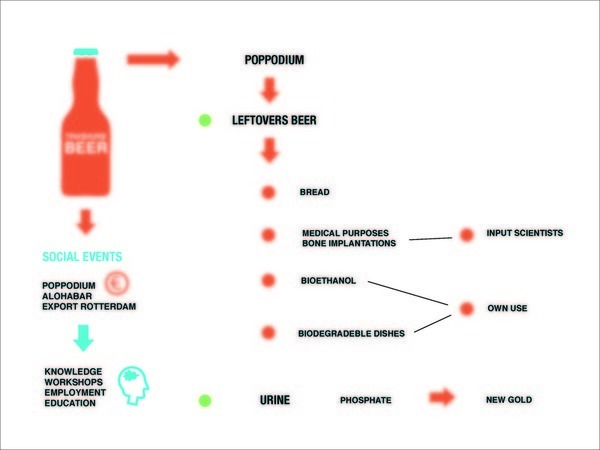
| − | + | [[File:mcce_stream4.jpg|Trashure Island generates food, drinks, compost, biogas (for cars) and knowledge for people. Money is generated from entrance fees and sales of produce to small businesses and individuals.]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {{#ev:youtube|1epFhxPLsf0}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ''The participating students came from: Bouwkunde minor dIB, Minor social practices WdKA and Cultural Economics, Erasmus University Rotterdam.'' | ||
| − | + | ''This masterclass was hosted and guided by Rotterzwam, organised by Floris Schiferli (Superuse Studios Rotterdam) and located in Tropicana, Maasboulevard 100, Rotterdam.'' | |
| − | + | ''With special thanks to: Mark Slegers & all co-workers of Rotterzwam (host and inspirer), Rechtstreex (for the lovely local lunch), Norbert Bol (Director of Grondmij capital investment), Mark Bode (Business Station WDKA), Hans Huurman (gemeente Rotterdam), Dave Geensen (poppodium Rotterdam).'' | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | + | {{Category selector | |
| − | + | |Category=Bottom-up | |
| − | + | }} | |
| + | {{Category selector | ||
| + | |Category=Economy | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Category selector | ||
| + | |Category=Circularity | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Category selector | ||
| + | |Category=Sustainability | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Category selector | ||
| + | |Category=Systems | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Category selector | ||
| + | |Category=Transformation | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Articles more}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:42, 31 October 2018
Author: Students Masterclass The Circular Economy
Tropicana, from a dream in decay to an opportunity for change?
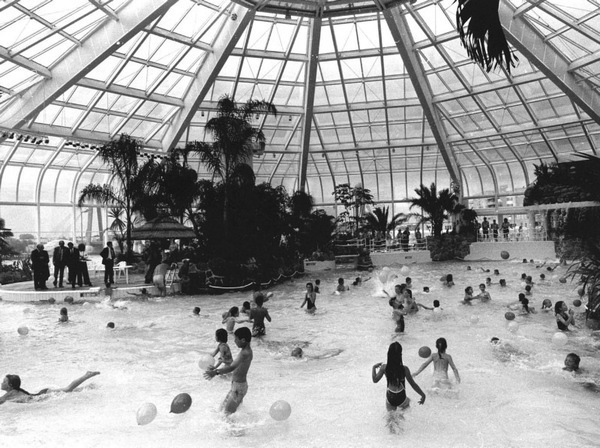
Over the past century, most cities have become agglomerations of monofunctional districts which are basically disconnected from each other. Residential neighbourhoods, industrial estates, office complexes, farming districts and recreational areas are spatially delimited by administrative boundaries, making it harder to make good use of their mutual presence. The ever-increasing flow of goods, energy, water, food and even capital is disconnected from the location where these are created, contributing to endless transportation, traffic congestion, waste of energy and pollution. In a special masterclass at the WdKA Redesigning Business event (November 2014), an interdisciplinary group of students sought ways to promote the exchange between existing flows by making smart new connections: the main requirement of an ecosystem. The host of this masterclass was Rotterzwam, a local mushroom farming business which grows mushrooms on left-over coffee grounds. We used their business case as a starting point for a proposal in which a former sub-tropical swimming paradise is turned into a centre for innovation: sustainable, connecting and regenerative.
The masterclass took place in Tropicana, an iconic building on the river Maas in Rotterdam that was built in 1988. It was a promise of a tropical experience, a true aquatic paradise. The lack of maintenance and plans to redevelop it into an event centre meant that Tropicana closed its doors in the summer of 2010. Bankruptcy in 2011 meant that the redevelopment never happened and the building became a dream in decay. At the moment though, smaller scale, but maybe more interesting, developments are happening on the site. It now serves as a temporary location for various businesses and has a restaurant and a bar as well as facilities for roasting coffee and farming oyster mushrooms on left-over coffee grounds. Can this landmark become a metaphor for new ways of thinking, sharing, working and relaxing all with an important focus on recycling as well as on research into flows of goods, energy, water, food and even capital? Can we make smart connections between local surpluses, shortages and bottlenecks, thus creating new functions and business cases for Tropicana?
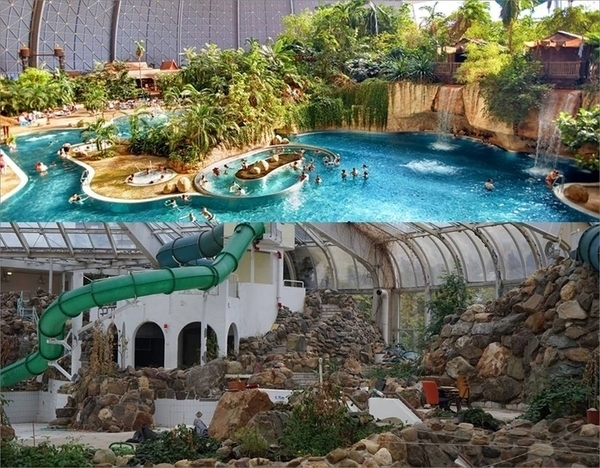
Trashure Island
The city of Rotterdam has high ambitions for sustainability. Why not use Tropicana as a building that represents sustainable development and give the building back its iconic status?! Tropicana could become 'Trashure Island', an island which will share and show sustainable ideas, mainly focussing on how to reuse waste flows. This would create a circular economy. It will be an ecosystem consisting of a lab and a knowledge centre where local people can learn by doing and where innovation and experimentation can take place. This way the mindset of people can change and it will be a new kind of education. This results in BIY: a Blue It Yourself economy. The waste flows of a concert stage, which will soon be added to the building, and the restaurant will also be a part of the circular ecosystem. The building's waste flows and trash and unemployed people become the new gold. Trash becomes treasure. It is an innovative way of creating awareness for sustainability for the people of Rotterdam and eventually for the rest of the world. This way, people can be introduced to the blue economy in an innovative and educative way (further explained in our video & images) and presentation of a case study in which we present Treasure Beer, a new beer brand that could be consumed as well produced in Tropicana (see video advertorial).
The participating students came from: Bouwkunde minor dIB, Minor social practices WdKA and Cultural Economics, Erasmus University Rotterdam.
This masterclass was hosted and guided by Rotterzwam, organised by Floris Schiferli (Superuse Studios Rotterdam) and located in Tropicana, Maasboulevard 100, Rotterdam.
With special thanks to: Mark Slegers & all co-workers of Rotterzwam (host and inspirer), Rechtstreex (for the lovely local lunch), Norbert Bol (Director of Grondmij capital investment), Mark Bode (Business Station WDKA), Hans Huurman (gemeente Rotterdam), Dave Geensen (poppodium Rotterdam).Links
CONTRIBUTE
Feel free to contribute to Beyond Social.