Sustainism
The wikipage input value is empty (e.g. SomeProperty::, [[]]) and therefore it cannot be used as a name or as part of a query condition.
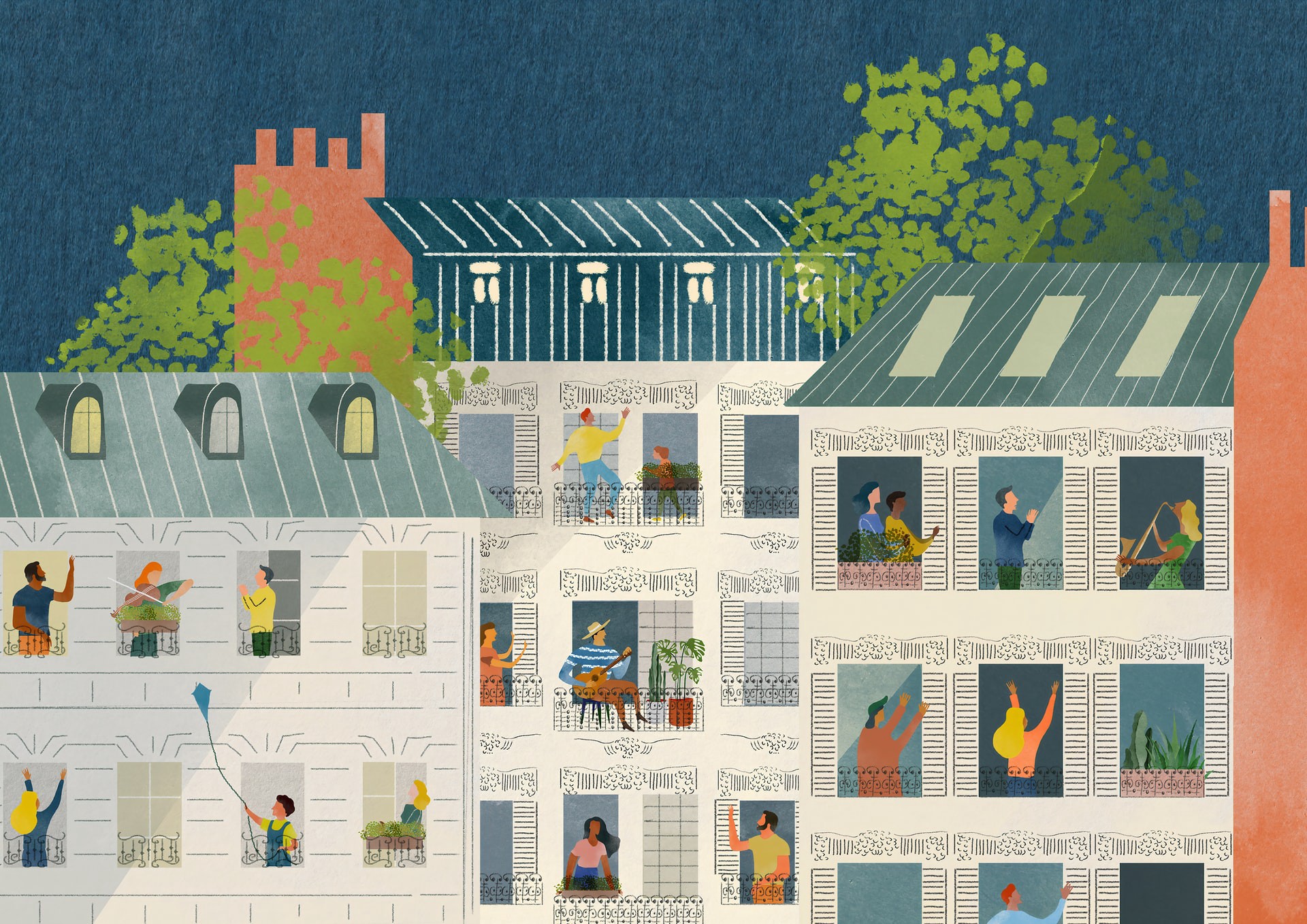
Sustainism includes every aspect that we as social beings deal with, from food to social media. In this new style of culture complex and diverse connections between local communities are formed to create an interwoven ‘web’ of humanity. The term, introduced by Joost Elffers and Michiel Schwarz, is represented by a trefoil knot, a knot created by tying the loose ends of a common knot together, a sign of interconnectedness. This symbol explains how in sustainism everything is connected and loops together, a circle of life.
Sustainism
A New Modernism
Local produce will become more accessible and sustainable lifestyles will become the new norm. Sustainism is built on the 4 principles of sharing, localism, connectedness and proportionality. The term sustainism already suggests a connection to the word ‘sustainability’, however, sustainism adds the layer of global and local connections to each other as humans by utilizing and sharing the technological advancements we have made over the decades. Proportionality comes in when sustainist design takes into consideration the broader picture, but knows how to scale their work in order for it to serve the greater good in the long run. For sustainist design, artists should initiate ideas and concepts that evoke human emotion, ideas that are shareable and scaled to be manageable within the designated community. (Schwarz & Diana, 2013) The concept of sustainism challenges innovators and creators to find creative solutions to link everything in our communities together and close the circularity gap in our economy.
Think of a local approach to living in a global world. Information and technology is open source and accessible for everyone, but the physical materials you need to survive are sourced locally. Regressive, since living in a community that is self-sufficient seems almost ancient, while being progressive by including our technological advances as human beings to connect ourselves intellectually and combine our knowledge. (Elfers & Schwarz, 2010)
Challenges
Though this new ideology sounds like a very logical way of living in this new age, it obviously comes with its challenges. With population growing consistently and overproduction is exhausting natural resources, materials have become scarce. To create self-sufficient local communities with the capabilities of the earth and technology in this age is something that would take years, maybe even decades to develop and innovate as well as be viable with the climate’s current state. (Verschuuren, Subramanian, & Hiemstra, 2014) The practical issues aside, to adapt this new model is not only a shift in the economic environment, it is also a social adaptation. Humans are social beings, through the course of history we have been conditioned to expand our presence over the entire world and focus on what makes us individuals. Early in history, human existence was built on hierarchy and who was the strongest, though throughout time this idea switched by introducing personal freedom and equality between all lives. Obviously there is still a long way to go, for human equality to be recognized worldwide, it does seem like humans are evolving to not rely on a social scale, but rather to have freedom of expression.
Sustainism would require humans to act in favour of the greater good, rather than putting themselves first as it is accustomed today. (COMPAS, 2007)
Examples
An example of emerging sustainism is a platform called Amsterdam Smart City, an online platform connecting the citizens of the Dutch capitol. Inhabitants can share their opinions on regulations, services etc. Municipalities and partners such as electricity providers can learn and network to optimize every resident’s lifestyle. This shows a balance between locality, being that the app concerns the city of Amsterdam, and the global possibilities of the digital sphere. (Amsterdam Smart City, n.d.)
Another sustainist concept emerged in 2001 in Washington D.C., a program titled ‘FabLab’. This initiative was introduced to research how information could be spread physically in underrepresented communities. A ‘FabLab’ is a small physical workspace that offers tools to create and learn. While the information and instructions to operate the machinery and tools in the workspace are shared within the online global community, the execution remains local and small scale. This open source program shows how communities can benefit from local spaces to produce small scale needs, while obtaining the knowledge from a global source. (Menichinelli, 2011)
Reflection
Taking everything into consideration, sustainism seems to be a quite simple approach to modern problems. However, it would take a lot of human adjusting and resource planning, for which, you need to have humanity on your side. In the examples mentioned, it shows that communities are still alive and actively looking for connections to optimize the collective lifestyle. Sustainism pushes for sustainability in a progressive way. It builds on our nature as social beings and our ability to share and innovate. Sustainism does challenge the current consumerist society, which is so ingrained in humans nowadays that it would be difficult to offer up an alternative that may seem more simplistic. Ultimately, sustainism is a term that was not ‘invented’ as much as it was given a name, as the balance between locality and global seems to be quite alive but in need of a collective boost. Reflecting on the term through the lens of my own life and the New Earth project, I learned that design does not always have to be artistic and ambitious in order to be effective. Solutions to modern problems can be very simple and accessible, it can actually be quite beneficial if it is. It is still important to try to evoke a sense of community with the design, to touch on what connects us as humans in order to inspire and motivate others. I think the principles of sharing, localism, connectedness and proportionality are aspects that I will often take into consideration in the future when I am thinking about design or other initiatives.
References
Amsterdam Smart City. (sd). Amsterdam Smart City. Opgehaald van Amsterdam Smart City: https://amsterdamsmartcity.com COMPAS. (2007). Learning Endogenous Development. Rugby : Practical Action Publishing. Elfers, J., & Schwarz, M. (2010). Sustainism is the New Modernism: A Cultural Manifesto for the Sustainist Era. New York: Distributed Art Publishers. Menichinelli, M. (2011, March 23). Business Models for FabLabs. Opgehaald van Openp2pdesign: http://www.openp2pdesign.org/2011/fabbing/business-models-for-fab-labs Schwarz, M., & Diana, K. (2013). Sustainist Design Guide. Amsterdam: BIS publishers.
Verschuuren, B., Subramanian, S. M., & Hiemstra, W. (2014). Community Well-being in Biocultural Landscapes Are We Living Well? Practical Action Publication.Links
CONTRIBUTE
Feel free to contribute to Beyond Social.
Sustainism
A New Modernism
The time for modernism is over, in today’s global conditions, it has become essential for us as a society to start looking at the bigger picture, and to start taking action. Sustainism includes every aspect that we as social beings deal with, from food to social media. In this new style of culture complex and diverse connections between local communities are formed to create an interwoven ‘web’ of humanity. The term, introduced by Joost Elffers and Michiel Schwarz, is represented by a trefoil knot, a knot created by tying the loose ends of a common knot together, a sign of interconnectedness. This symbol explains how in sustainism everything is connected and loops together, a circle of life.
Local produce will become more accessible and sustainable lifestyles will become the new norm. Sustainism is built on the 4 principles of sharing, localism, connectedness and proportionality. The term sustainism already suggests a connection to the word ‘sustainability’, however, sustainism adds the layer of global and local connections to each other as humans by utilizing and sharing the technological advancements we have made over the decades. Proportionality comes in when sustainist design takes into consideration the broader picture, but knows how to scale their work in order for it to serve the greater good in the long run. For sustainist design, artists should initiate ideas and concepts that evoke human emotion, ideas that are shareable and scaled to be manageable within the designated community. (Schwarz & Diana, 2013) The concept of sustainism challenges innovators and creators to find creative solutions to link everything in our communities together and close the circularity gap in our economy.
Think of a local approach to living in a global world. Information and technology is open source and accessible for everyone, but the physical materials you need to survive are sourced locally. Regressive, since living in a community that is self-sufficient seems almost ancient, while being progressive by including our technological advances as human beings to connect ourselves intellectually and combine our knowledge. (Elfers & Schwarz, 2010)
Challenges
Though this new ideology sounds like a very logical way of living in this new age, it obviously comes with its challenges. With population growing consistently and overproduction is exhausting natural resources, materials have become scarce. To create self-sufficient local communities with the capabilities of the earth and technology in this age is something that would take years, maybe even decades to develop and innovate as well as be viable with the climate’s current state. (Verschuuren, Subramanian, & Hiemstra, 2014) The practical issues aside, to adapt this new model is not only a shift in the economic environment, it is also a social adaptation. Humans are social beings, through the course of history we have been conditioned to expand our presence over the entire world and focus on what makes us individuals. Early in history, human existence was built on hierarchy and who was the strongest, though throughout time this idea switched by introducing personal freedom and equality between all lives. Obviously there is still a long way to go, for human equality to be recognized worldwide, it does seem like humans are evolving to not rely on a social scale, but rather to have freedom of expression.
Sustainism would require humans to act in favour of the greater good, rather than putting themselves first as it is accustomed today. (COMPAS, 2007)
Examples
An example of emerging sustainism is a platform called Amsterdam Smart City, an online platform connecting the citizens of the Dutch capitol. Inhabitants can share their opinions on regulations, services etc. Municipalities and partners such as electricity providers can learn and network to optimize every resident’s lifestyle. This shows a balance between locality, being that the app concerns the city of Amsterdam, and the global possibilities of the digital sphere. (Amsterdam Smart City, n.d.)
Another sustainist concept emerged in 2001 in Washington D.C., a program titled ‘FabLab’. This initiative was introduced to research how information could be spread physically in underrepresented communities. A ‘FabLab’ is a small physical workspace that offers tools to create and learn. While the information and instructions to operate the machinery and tools in the workspace are shared within the online global community, the execution remains local and small scale. This open source program shows how communities can benefit from local spaces to produce small scale needs, while obtaining the knowledge from a global source. (Menichinelli, 2011)
Reflection
Taking everything into consideration, sustainism seems to be a quite simple approach to modern problems. However, it would take a lot of human adjusting and resource planning, for which, you need to have humanity on your side. In the examples mentioned, it shows that communities are still alive and actively looking for connections to optimize the collective lifestyle. Sustainism pushes for sustainability in a progressive way. It builds on our nature as social beings and our ability to share and innovate. Sustainism does challenge the current consumerist society, which is so ingrained in humans nowadays that it would be difficult to offer up an alternative that may seem more simplistic. Ultimately, sustainism is a term that was not ‘invented’ as much as it was given a name, as the balance between locality and global seems to be quite alive but in need of a collective boost. Reflecting on the term through the lens of my own life and the New Earth project, I learned that design does not always have to be artistic and ambitious in order to be effective. Solutions to modern problems can be very simple and accessible, it can actually be quite beneficial if it is. It is still important to try to evoke a sense of community with the design, to touch on what connects us as humans in order to inspire and motivate others. I think the principles of sharing, localism, connectedness and proportionality are aspects that I will often take into consideration in the future when I am thinking about design or other initiatives.
References
Amsterdam Smart City. (sd). Amsterdam Smart City. Opgehaald van Amsterdam Smart City: https://amsterdamsmartcity.com COMPAS. (2007). Learning Endogenous Development. Rugby : Practical Action Publishing. Elfers, J., & Schwarz, M. (2010). Sustainism is the New Modernism: A Cultural Manifesto for the Sustainist Era. New York: Distributed Art Publishers. Menichinelli, M. (2011, March 23). Business Models for FabLabs. Opgehaald van Openp2pdesign: http://www.openp2pdesign.org/2011/fabbing/business-models-for-fab-labs Schwarz, M., & Diana, K. (2013). Sustainist Design Guide. Amsterdam: BIS publishers. Verschuuren, B., Subramanian, S. M., & Hiemstra, W. (2014). Community Well-being in Biocultural Landscapes Are We Living Well? Practical Action Publication.